What Is Allergy Testing?
Allergy testing and treatment Healthcare providers can perform allergy testing which helps them recognize allergens that might be causing symptoms.
These tests aid healthcare providers in evaluating how you respond to pollen, pet dander, mold, bee stings, peanuts, and myriad other stimuli. Allergy testing and treatment Allergy testing and treatment
Following your tests, your provider will devise plans for helping you manage your symptoms.
Common Allergens
Allergy testing helps in identifying a broad range of possible allergens which include mold, pet dander, and pollen. Others may react to insect estings, certain foods such as peanuts or milk, and even latex.Late allergy testing will assist in recognizing the sources in order to avoid them.Allergy testing and treatment
Types of Allergy Tests
As technology progresses, healthcare providers have more and more tools available. Symptoms, age, and the allergens you have may determine what type of allergy test is used.
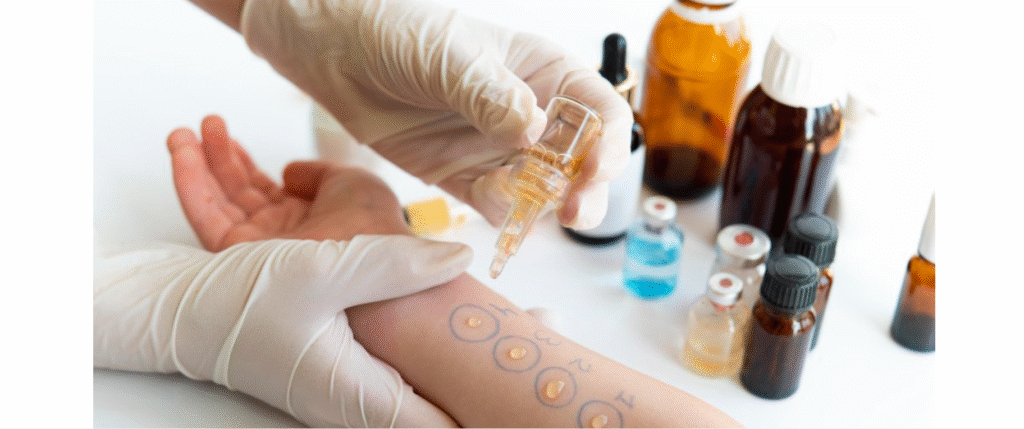
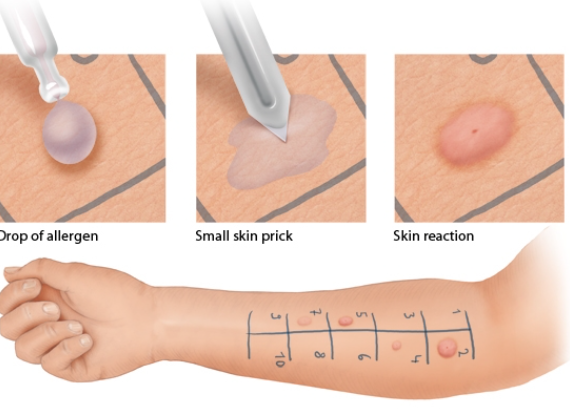
Skin Prick (Scratch) Test: By far the most popular test. A healthcare provider uses a small needle and pricks the patient’s skin with a potential allergen.
If an allergy is present, redness and swelling will occur and raised bumps known as wheals will appear within a quarter hour.
Intradermal Skin Test: Conducted when the skin prick test does not yield definitive results. An allergen is injected in the periphery of the skin as a small bubble. It is useful to appreciate the sensitization to drugs, insect stings, or dust particles.
Patch Test:
Useful for diagnosing contact dermatitis. A patch containing allergens is placed on the skin for 48 to 96 hours. Delayed reactions are checked by your provider after the patch has been removed.
Blood (IgE) Test: A sample of blood is taken and analyzed in a laboratory for IgE antibodies that correspond to certain allergens. It measures both total and specific IgE levels.
Under careful medical supervision, small doses of the suspected allergen are given to the individual in this Oral Food Challenge to see if a reaction triggers. This test is primarily done for food or drug allergies.

Importance of Allergy Testing
Allergy testing aids in the diagnosis of conditions like allergic rhinitis, food allergy, allergic asthma, and others.
It is also vital for patients who sustain a serious allergic reaction like anaphylaxis that may include hives, breathing difficulties, or an abrupt decrease in blood pressure. Allergy testing and treatment
Allergen identification, in this case, is essential for appropriate intervention and management and is even life-saving in some situations.Allergy testing and treatment
When to Consider Tests for Allergies
If a patient experiences symptoms of allergies frequently without a clear explanation, testing can be a solution. Possible symptoms might be:
Allergies by Air (for example, dust, pollen):
Sore throat or coughing or blocked nose
Watery eyes that hurt
Pain, discomfort, or soreness in the head
Wheezing or coughing
Food Allergies:

Details of Allergy Test
Skin reactions, like swelling, hives or itching
Digestive problems such as cramps, nausea
Such as: Respiratory And Cardiovascular Symptoms Like Dizziness
Contact Allergies Such As: Latex, And Certain Metals
Rashes on the skin, itchiness, burning sensations, or blisters
Take note of every symptom. Even mild allergic responses can become life-threatening without any warning. An accurate diagnosis is critical in eliminating complications later on.
Details of Allergy Test
The way an allergen is tested.Allergy testing and treatment
Allergy tests determine the reactivity of your immune system toward a certain allergen. If reactive, the body releases IgE antibodies [performs an allergic reaction] which precipitate the release of certain chemicals resulting in allergic symptoms.
Preparing for testing requires no special preparation other than fasting and stopping some medications. For example, antihistamines taken a few days before the test may be detrimental toward the test results. However, the medication controlling asthma is to be continued unless stated otherwise.
During test procedures, mild allergic symptoms of redness and itching might be develop from skin tests, but these usually subdue a few hours later.
Blood work consists of drawing blood from a vein and that is done quickly.Allergy testing and treatment
Challenging a drug or food is done under close supervision in case the person reacting severely.
Course Duration Allergy testing and treatment
Blood work: Done in ten minutes.
Skin prick/intradermal tests: Done in three to five minutes for each allergen, results are observed for 15 to 20 minutes.
Patch tests: Done and applied in the office, checked in forty-eight to ninety-six hours later.
Food challenges: Up to three to four hours.
What Does a Full Panel Allergy Test Include:
A wide ranging test panel checks for typical allergens from pollen such as:mold, dust mites, and pet dander are but a few examples. This extensive testing identifies several triggers within a single appointment.
Risks and Results
While anaphylaxis during testing is unlikely, serious reactions can occur. For this reason, all testing takes place in a medical facility with emergency support. Itching is the most common reaction and is easy to treat.
When Will You Receive Results?
Skin prick tests: results available immediately
Blood tests: within a week or more
Patch tests: 2-4 days after test
Interpreting Results
Negative: you are most probably not allergic to the tested substance
Positive: some level of sensitivity exists but it’s not always symptomatic. Some tests may produce false positives, particularly blood IgE tests.
Managing Allergen Exposure After Diagnosis
If you test positive for an allergy, the following steps might be put in place by your provider:
Avoiding allergens: Known triggers, especially those that cause severe reactions, should be limited.
Taking medications: Some of the symptoms could be managed using prescribed antihistamines or nasal sprays.
Administration of allergy shots (immunotherapy): long-term treatment aimed at reducing immune sensitivity – commonly three to five years.
Medical ID and other medication: Patients with severe allergies should be equipped with an epinephrine autoinjector (e.g., EpiPen®), a medical alert bracelet, or a card as these are crucial in case of emergencies.
Common Questions Answered
Do At-Home Allergy Tests Work?
At-home tests are less accurate than those performed in a clinic. They often provide false positives and may not test the correct antibodies. See a healthcare provider for appropriate diagnosis.
Are Allergy Tests Covered by Insurance?
They do not provide uniform coverage. Check with your insurance provider for details on what is included in your plan and what the uncovered costs will be.
What’s The Right Age For Allergy Testing?
Testing can be done on adults and older children. However skin testing is usually not recommended under the age of 6 months. Children under five may not have blood test accuracy; however testing decisions are made based on individual symptoms and their medical history.





